Diskless netboot
Contents
Target folder tree (server side)
This is how we'll setup our files and folders:
# TFTP root
/tftpboot/
###############
# Network bootable image(s) using NFS technology
################
#### Boot file
/tftpboot/pxelinux.0 # Initial boot file - only use to load the PXE NetBoot manager
/tftpboot/{menu.c32 || vesamenu.c32} # PXE interactive menu managers (text or graphical)
/tftpboot/pxelinux.cfg/ # PXE configuration(s)
/tftpboot/pxelinux.cfg/default # default PXE configuration
#### Kernel file
/tftpboot/images/
# Debian 7.x [Wheezy]
/tftpboot/images/wheezy/
/tftpboot/images/wheezy/vmlinuz
/tftpboot/images/wheezy/initrd.img
# [X]Ubuntu 14.04 [Trusty]
/tftpboot/images/trusty/
/tftpboot/images/trusty/vmlinuz
/tftpboot/images/trusty/initrd.img
#### NFS
# This is where the runnable will be. Each image will be in a dedicated folder.
/nfs/
# Debian 7.x [Wheezy]
/nfs/wheezy/
# Ubuntu 14.04 [Trusty]
/nfs/trusty/
Client overview
Each client must have, at least, 4 Go of RAM.
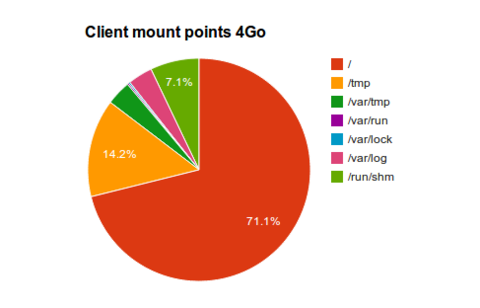
4 GO RAM configuration
This is how we're gonna populate the client:
As you can see, each client will have some space dedicated for swap + some RAMdisk to allow writing in /var, /tmp and /proc.
Configuration of a 4Go RAM disk:
- No swap
- Local TMPFS (read/write for /dev, /tmp, ...) : 1 Go
- /tmp = 512 M
- /var/tmp = 128 M
- /var/log = 128 M
- /var/run = 8 M
- /var/lock = 8 M
- /run/shm = 256 M
- O.S (NFS read only) : all the rest ~ 2.8 Go
- Common share (NFS read write) : Remote disk
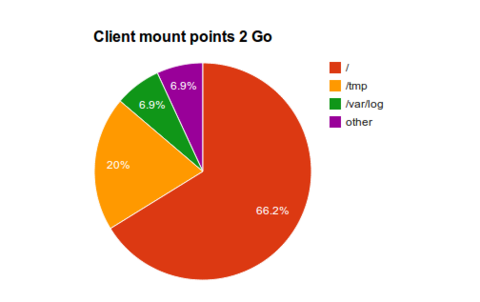
2 Go
Due to budget restriction we might encounter some low memory machines with only 2 Go...
This is how we're gonna populate the client:
In case of 2Go RAM then you have to use some tricks:
- No swap
- O.S (NFS read only) : ~ 1.2 Go
- Common share (NFS read write) : Remote disk
- Local TMPFS (read/write for /dev, /tmp, ...) : all the rest
- /tmp = 372 M
- /var/tmp = auto
- /var/log = 128 M
- /var/run = auto
- /var/lock = auto
- /run/shm = auto
How big is the client image ?
By default the deboostrap Ubuntu 14.04 LTS image is 239 Mo. With the applications we're gonna use that size will increase to about 1 or 1.3 Go depending if you copy (or not) the kernel sources. It may even take 1.6 Go if you're using XFCE frontend.
NFS client image
There are different way to setup a NFS client image.
The main ones are:
- Manually
- debootstrap
- copying the install from your server
- Manual install on a client, then, when the system is ready, copy everything to the NFS share
- Using script and software like "Puppet" or "Chef"
Setup client distribution
You have to create one target for each distribution you want to serve:
mkdir -p /nfs/trusty
mkdir -p /nfs/wheezy
mkdir -p /nfs/common
- NOTES -
- The folder name should match your NetBoot settings. Folder name = a LABEL in the NetBoot config.
- The folder name should match a Linux (Debian like) distribution name
Configure client distribution
- Manual configuration: Diskless image configuration - manual setup
- Automatic [Puppet || Chef] configuration: Diskless image configuration - script setup
Backup distribution
You can create an archive of your current distribution for later restore / re-use.
Compression
cd /nfs
tar cvpjf trusty.tar.bz2 ./trusty
Restoration
cd /nfs
tar -xvjf trusty.tar.bz2You can create interactive NetBoot menus, see:
Local server monitoring
Install the following services:
Other services
File sharing
If you want to expose the NFS common folder as a file-share, you have to install and configure Samba. See: Samba server
Note
Samba is actually better than NFS for the file-share. You should remove Common from /etc/exports and use a samba share instead.
Management UI (webmin)
Since there is a lot of services to manage, it's always convenient to use an UI for it. Check Webmin
VPN server
See VPN
Apache2 server
See Apache 2
References
Ubuntu diskless how-to: https://help.ubuntu.com/community/DisklessUbuntuHowto
Mind reference: http://mindref.blogspot.se/2011/03/debian-diskless.html
Super video tutorials:
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=js9imsrqAMk
- http://www.stepladder-it.com/bivblog/14/ to /16/
- https://blog.dlasley.net/2013/01/pxe-server-ubuntu/
Nice explanation of PXE process: http://www.linux.com/learn/docs/ldp/497-Diskless-root-NFS-HOWTO
- How to improved /etc/fstab: http://www.askapache.com/optimize/super-speed-secrets.html